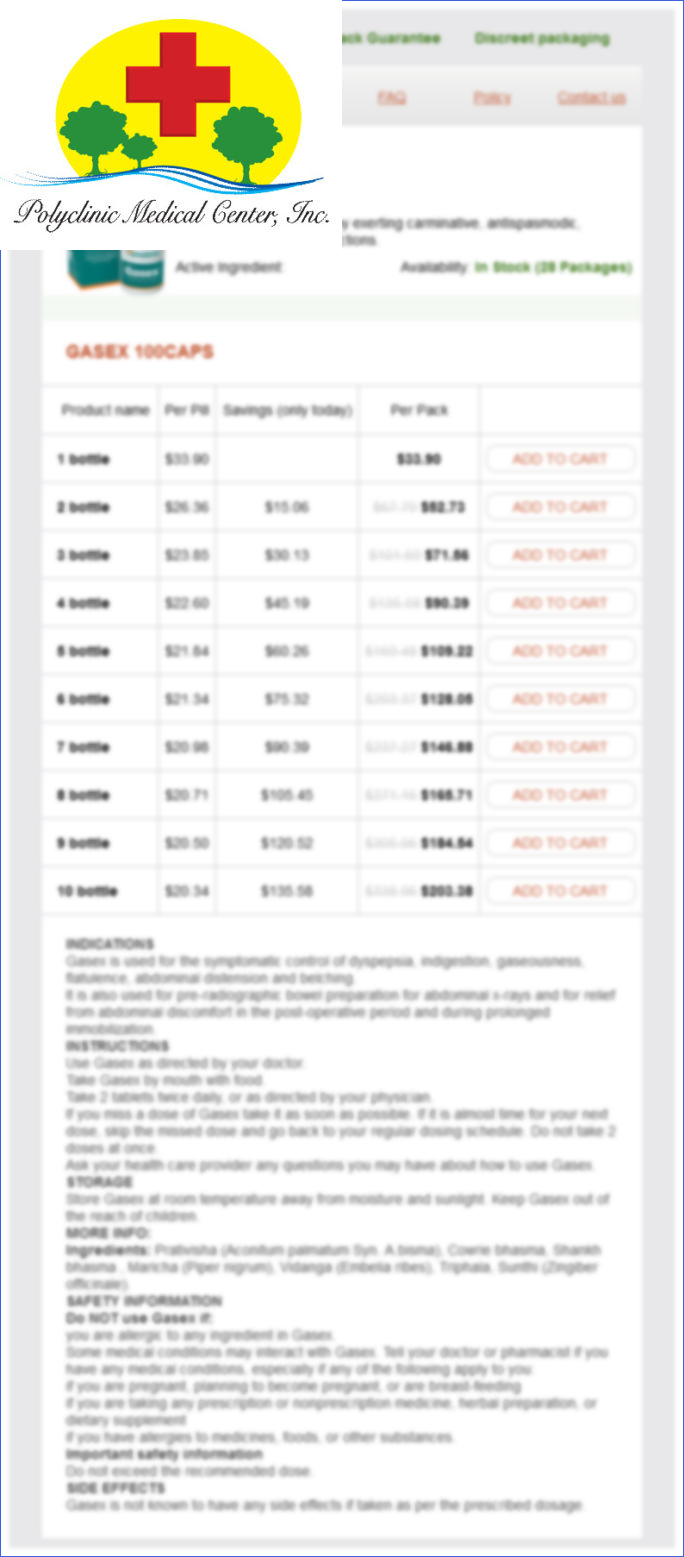
Gasex dosages: 100 caps
Gasex packs: 1 bottle, 2 bottle, 3 bottle, 4 bottle, 5 bottle, 6 bottle, 7 bottle, 8 bottle, 9 bottle, 10 bottle
Only $21.61 per item
In stock: 567
Description
Peritonitis-Inflammation of the layer of tissue that lines the inside of the abdominal cavity gastritis diet ýëåêòðîííîå 100 caps gasex purchase free shipping. Thrombophlebitis-Inflammation of the veins, usually in the legs, which causes swelling and tenderness in the affected area. Morbidity and mortality rates the mortality rate of appendicitis has dramatically decreased over time. According to the Merck Manual, the mortality rate is estimated at less than 1% with timely surgery. Death is usually due to peritonitis, intra-abdominal abscess, or severe infection following rupture. Alternatives Appendectomies are usually carried out on an emergency basis to treat appendicitis. Due to the serious consequences of not removing an inflamed appendix, which include rupture and peritonitis, there are no alternatives to appendectomy. Many patients are discharged from the hospital within 24 hours after the appendectomy. The disorder is most common in people between the ages of 10 and 30, but it can develop at any age. It is more common in men than in women, however; the male/female ratio is about 1. Although appendicitis is not hereditary, it does appear to be more common in some families; in 2009, a team of Australian researchers reported a possible link to chromosome 1p37. About 1 person in every 100,000 is born without an appendix; there are a few rare cases of persons born with two. Appendicitis Definition Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, which is the worm- or finger-shaped pouch attached to the cecum, the beginning of the large intestine. Appendicitis is a medical emergency, and if it is left untreated the appendix may rupture and cause a potentially fatal infection. Demographics Appendicitis was the most common abdominal emergency in children and young adults in Canada and the United States as of 2010. The National 488 Description the average human appendix ranges in size from about 3 inches in length to 4 or 5 inches, but appendices as long as 11 inches have been recorded. This blockage can be caused by a number of different objects ranging from intestinal parasites to thick mucus or fecal matter, or an infection. As the blockage progresses, the tissues of the appendix begin to die from lack of blood flow. If the condition is not treated, the appendix swells and eventually bursts, spreading the infection throughout the abdomen. This spread of infection and inflammation to the tissues lining the abdomen is called peritonitis and is a very dangerous condition. The pain of appendicitis usually starts two to three days before the appendix gets to the point of bursting.
Syndromes
- The surgeon makes another surgical cut and passes tools through this opening. A small pointed tool called an awl is used to make very small holes in the bone near the damaged cartilage. These are called microfractures.
- Umbilical cord problems
- Tuberculosis of the kidney and infections related to AIDS
- Mammary fat necrosis
- Fistula (abnormal passage) between the vagina and the skin
- Dizziness
- Conditions involving the muscles and the nerves that control them (myasthenia gravis)
- Metolazone (Zaroxolyn, Diulo)
- Vomiting
An intravenous line is inserted so that medications (anticoagulants to prevent clot formation and radioactive dye for x rays) can be administered gastritis jelentese gasex 100 caps buy fast delivery. About an hour before the procedure, the patient is given an oral sedative such as diazepam (Valium) to ensure that he or she will relax sufficiently for the procedure. Balloon valvuloplasty Aftercare After balloon valvuloplasty, the patient will spend several hours in the recovery room to be monitored for vital signs (such as heart rate and breathing) and heart sounds. For at least 30 minutes after removal of the catheter, direct pressure is applied to the site of insertion; after this, a pressure dressing will be applied. Intravenous fluids will be given to help eliminate the x-ray dye; intravenous anticoagulants or other medications may be administered to improve blood flow and to keep coronary arteries open. Some patients will continue to take anticoagulant medications for months or years after the surgery and will have regular blood tests to monitor the effectiveness of the medication. Following discharge from the hospital, the patient can usually resume normal activities. After balloon valvuloplasty, lifelong follow-up is necessary because valves sometimes degenerate or narrowing recurs, a condition called restenosis, which will likely require repeat valvuloplasty, valvotomy, or valve replacement. An area on the inside of the upper leg will be washed and treated with an antibacterial solution to prepare for the insertion of a catheter. The patient is given local anesthesia to numb the insertion site and will usually remain awake, able to watch the procedure on the monitor. After the insertion site is prepared and anesthetized, the cardiologist inserts a catheter into the appropriate blood vessel, and then passes the smaller balloon-tipped catheter through the first catheter. Guided by the x-ray monitor that allows visualization of the catheter in the blood vessel, the physician slowly threads the catheter up into the coronary artery to the heart. The deflated balloon is carefully positioned in the opening of the valve that is being treated, and then is inflated repeatedly, which applies pressure to dilate the valve. The inflated balloon widens the valve opening by splitting the valve leaflets apart. The other catheter remains in place for 6Â12 hours because, in some cases, the procedure must be repeated. A double-balloon valvuloplasty procedure is often performed on certain high-risk patients because it is considered more effective in restoring blood flow. For example, the valve can become misshapen so that it does not close completely, which makes the condition worse. Embolism, where either clots or pieces of valve tissue break off and travel to the brain or the lungs causing blockage, is another possible risk. If the procedure causes severe damage to the valve leaflets, immediate valve replacement is required.
Specifications/Details
Gun-Ji-Whang (Rehmannia). Gasex.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Rehmannia.
- How does Rehmannia work?
- Diabetes, anemia, fever, osteoporosis, allergies, or other conditions.
- What is Rehmannia?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97099
In practice gastritis not healing purchase gasex 100 caps on line, malabsorptive surgery is combined with some type of restrictive surgery so that less food is also moving through the digestive tract. In this surgery, a small stomach pouch is created by stapling and banding the stomach. Next, a Y-shaped piece of intestine is attached to the pouch on one end, and the jejunum, or second part of the small intestine, on the other. This allows food to bypass the duodenum, or first part of the intestine where many calories and nutrients are absorbed. The great advantage of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is that individuals lose on average 60Â70% of their excess weight and are able to maintain the weight loss for 10 years or more. As a result, most obesity-related health problems are substantially reduced or cured when weight is lost and weight loss maintained. Disadvantages are the same as for Roux-en-Y surgery, but nutrient deficiencies are greater. Bariatric surgery Purpose Obesity is the second leading cause of preventable death in the United States. Adults age 20 and older are evaluated as follows: this surgery is more difficult for the surgeon than restrictive surgeries and involves permanently altering the digestive system. Tearing, bleeding, and infection at the sites where the cuts and reconnections were made are potentially fatal complications. This level of obesity is often referred to as morbid obesity as it can result in many serious, and potentially deadly, health problems. Bariatric surgery is performed only on people whose risk of complications from surgery is outweighed by the need to lose weight to prevent health complications and for whom supervised weight-loss and exercise programs have repeatedly failed. Heartburn-A pain in the center of the chest behind the breastbone caused by the contents of the stomach backflowing (refluxing) into the lower end of the esophagus and causing irritation. Morbidly obese-Defines a person who is 100 lb (45 kg) (or more than 50%) overweight and has a body mass index above 40. Osteoporosis-A condition found in older individuals in which bones decrease in density and become fragile and more likely to break. Sleep apnea-A sleep disorder in which breathing stops briefly then resumes on its own. Type 2 diabetes-Sometimes called adult-onset diabetes, a disease that prevents the body from properly using glucose (sugar) but can often be controlled with diet and exercise. Pre-surgery counseling is required to help patients anticipate what to expect after the operation. Aftercare Immediately after the operation, most patients are restricted to a liquid diet for 2Â3 weeks; however, some may remain on it for up to 12 weeks.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q.d.
Tags: generic 100 caps gasex mastercard, cheap gasex 100 caps overnight delivery, cheap gasex 100 caps mastercard, buy discount gasex 100 caps on-line
8 of 10
Votes: 169 votes
Total customer reviews: 169
Testimonials
Bozep, 61 years: Cirrhosis-Disruption of liver function due to damage from chronic progressive disease. Treating anorexia is often a long, slow, frustrating process that can cost thousands of dollars.
Innostian, 64 years: Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia-A severe lung infection caused by a parasitic protozoan. While each drug works slightly differently, they generally work by increasing the availability of certain neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, or serotonin, in the brain.

 Contact
Contact Hours
Hours Location
Location