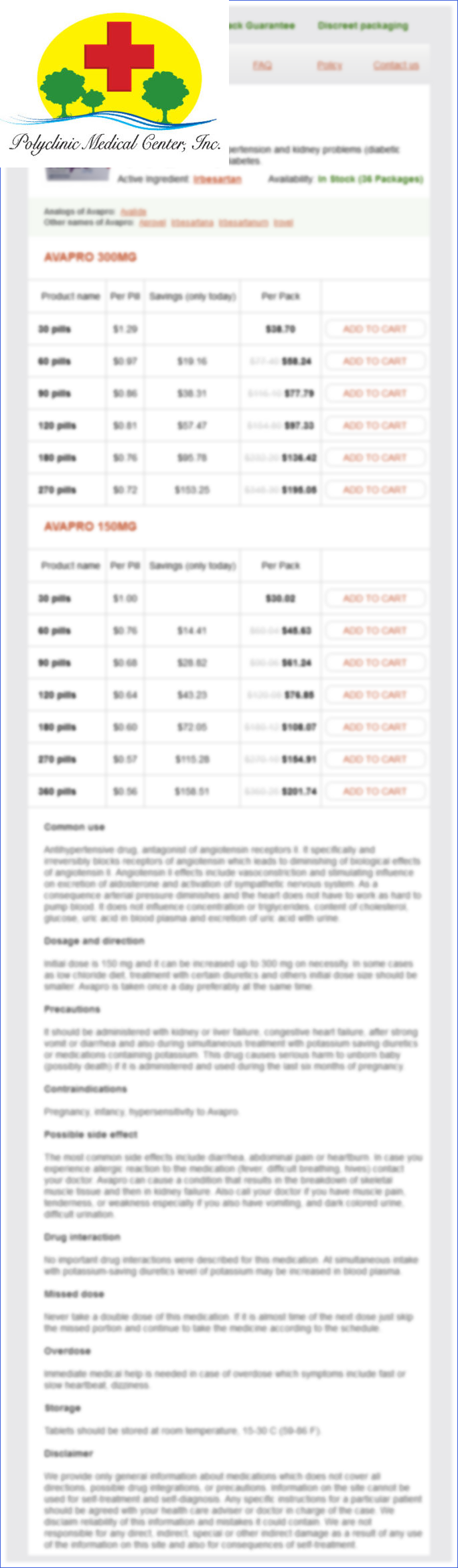
Avapro dosages: 300 mg, 150 mg
Avapro packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Only $0.6 per item
In stock: 881
Description
Maintaining a relatively high index of suspicion and completing a careful history and physical examination may enhance the ability of the clinician to detect these and other medical conditions in a patient who has limited ability to communicate and who may exhibit aberrant behaviors at baseline diabetic diet 1500 calories exchange chart 150 mg avapro buy amex. The challenging behavior can take on an operant, or learned, function that persists after resolution of the initial medical condition. After treatable medical causes and modifiable behavioral and environmental factors have been ruled out or addressed, a therapeutic trial of medication directed at specific target symptoms or behaviors may be considered. Literature reviews have summarized the evidence pertaining to psychopharmacological management, the details of which are beyond the scope of this chapter. Clinicians should carefully weigh potential risks and benefits, use psychotropic medications as part of a comprehensive treatment approach, and only prescribe medications with which they have sufficient expertise, including knowledge of indications and contraindications, dosing, potential adverse effects, drug-drug interactions, and monitoring requirements. American Academy of Pediatrics Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 454 Table 19. Regardless of their level of intellectual functioning, these individuals continue to experience difficulty with social relationships, independent living, employment, and mental/behavioral health. It is not clear whether this is attributable to interventions, the nature of the original clinical presentation, intrinsic/genetic predisposition to a highly atypical developmental trajectory, or perhaps resolution of an interfering process. Despite the excellent outcomes in this group, there is a high rate of persisting difficulties in social understanding, pragmatic language, attention, emotional maturity and self-control, and psychiatric symptoms and diagnoses. Primary pediatric health care professionals play an important role in identification and management of children with this common neurodevelopmental disorder. Although no clinically useful biological markers have been identified, substantial advances have been made in characterizing the genetics, neurobiology, and neuropsychology of this heterogeneous disorder. A multisite study of the clinical diagnosis of different autism spectrum disorders. Changes in prevalence of parent-reported autism spectrum disorder in school-aged U. Estimated prevalence of autism and other developmental disabilities following questionnaire changes in the 2014 National Health Interview Survey. Autism spectrum disorders in the Stockholm Youth Cohort: design, prevalence and validity. The increasing prevalence of reported diagnoses of childhood psychiatric disorders: a descriptive multinational comparison. Autistic spectrum disorders: changes in the California caseload: an update: June 1987June 2007. Comorbidity of intellectual disability confounds ascertainment of autism: implications for genetic diagnosis. Explaining the increase in the prevalence of autism spectrum disorders: the proportion attributable to changes in reporting practices.
Syndromes
- Headache
- Poultry, pork, and shellfish
- Feeling extremely tired for more than 24 hours after exercise that would normally be considered easy
- Jaundice
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical conditions, your surgeon will ask you to see your doctor who treats you for these conditions.
- This type of formula may be helpful for infants who have true allergies to milk protein, and for those with skin rashes or wheezing caused by allergies.
- Spinal cord injury
- Decreased urine output (may stop completely)
- Heart disease
Oro-facial motor incoordination may make speech and swallowing difficult and drooling is a frequent problem; none of these defects implies a poor intellect although far too frequently the wrong conclusions are drawn managing diabetes at night cheap 150 mg avapro free shipping. However, the factors that damage the motor centres may also cause damage to other areas of the developing brain and thus many children with cerebral palsy have associated problems such as epilepsy (3040%), impaired vision and/or hearing, significant learning difficulties (30%) and perceptual and behavioural problems. Bilateral · Diplegia involves both sides of the body, with the lower limbs always most severely affected. Side-to-side involvement may be asymmetrical and the terms asymmetric diplegia and occasionally bilateral hemiplegia are used. The less severely affected children can have reasonable mobility but the non-walking diplegic patient may be similar to the total body involvement group discussed below. Patients usually have significant associated problems, such as difficulty swallowing and epilepsy, and they are wheelchair-based. The Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe collaboration recommends describing distribution as unilateral or bilateral and classifies the main motor tone types into one of four groups: spastic, dyskinetic, ataxic and mixed. This usually appears as a spastic palsy on one side of the body with the upper limb more severely affected than the lower. True monoplegia is so unusual that other diagnoses should be considered, such as a neonatal brachial plexopathy. It is characterized by a velocity-dependent increased muscle tone and hyper-reflexia. The resistance to passive movement may obscure a basic weakness of the affected muscles. There are two main types: Dystonic characterized by hypokinesia (reduced activity) and hypertonia (increased tone) resulting in stiff movements Choreoathetotic characterized by hyperkinesia (increased activity) and hypotonia (reduced tone) resulting in uncoordinated writhing and jerky movements. In pure athetoid cerebral palsy, joint contractures are unusual as muscle tone is not increased. In addition to these four main types, the following clinical picture is frequently seen: · Hypotonia, which is usually (but not always) a phase, lasting several years during early childhood, before the features of spasticity become obvious. If surgical treatment is being considered, it should never be based on a single assessment when, due to stress, the child appears to have abnormally high tone and muscle contractures: if seen again the following day, the clinical picture could be very different. The five reflexes that Bleck suggested we look for are: (1) the primitive neck-righting reflex, (2) asymmetrical and (3) symmetrical tonic neck reflexes, (4) the Moro reflex and (5) the extensor thrust response. Early symptoms include difficulty in sucking and swallowing, and excessive drooling. The normal child develops head control at 3 months, sits up at 6 months and begins walking at about 1 year. A history of a pre- or peri-natal event such as a premature birth, difficult labour or fetal distress should arouse suspicion. Diagnosis in later childhood Most children presenting to the orthopaedic surgeon have already had the diagnosis made. Ideally, the child should be reviewed by a multidisciplinary team so that feeding, speech, hearing, visual acuity, intelligence and motivation can also be assessed. Since cerebral palsy is essentially a disorder of posture and movement, the child should be carefully observed sitting, standing, walking and lying.
Specifications/Details
Areca Palm (Areca). Avapro.
- How does Areca work?
- Schizophrenia, glaucoma, or aiding in digestion.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Areca?
- Dosing considerations for Areca.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96956
If the patient consistently stands with one knee bent (even though his legs are equal in length) diabetic jewish diet generic 150 mg avapro amex, this suggests nerve root tension on that side; flexing the knee relaxes the sciatic nerve and reduces the pull on the nerve root. Then ask him to lean backwards (extension) (b), forwards to touch his toes (flexion) (c) and then sideways as far as possible (d), comparing his level of reach on the two sides. Finally, hold the pelvis stable and ask the patient to twist first to one side and then to the other (rotation). Note that rotation occurs almost entirely in the thoracic spine (e) and not in the lumbar spine. With a stiff back the movement occurs at the hips and there may be no spinal excursion. The mode of flexion (whether it is smooth or hesitant) and the way in which the patient comes back to the upright position are also important. With mechanical back pain, the patient tends to regain the upright position by pushing on the front of their thighs. To test extension, ask the patient to lean backwards, without bending their knees. Lateral flexion is tested by asking the patient to bend sideways, sliding their hand down the outer side of the leg; the two sides are compared. The patient in (a) has ankylosing spondylitis and a rigid lumbar spine, but he is able to reach his toes because he has good flexibility at the hips. With the patient upright, select two bony points 10 cm apart and mark the skin (b); as the patient bends forward, the two points should separate by at least a further 5 cm (c). Rib-cage excursion is assessed by measuring the chest circumference in full expiration and then in full inspiration; the normal difference is about 7 cm. Ask the patient to stand on their toes (plantarflexion) and on their heels (dorsiflexion) as a useful screen for motor power in the legs; small differences between the two sides are easily spotted. Again, look for localized deformities and muscle spasm, and examine the buttocks for gluteal wasting. The popliteal and posterior tibial pulses are felt, hamstring power is tested and sensation on the back of the limbs assessed. A rapid appraisal of the thyroid, chest (and breasts), and abdomen (and scrotum) is advisable, and essential if there is even a hint of generalized disease. Hip and knee mobility are assessed before testing for spinal cord or root involvement. With a straight knee, the leg is slowly raised until pain is produced not merely in the lower back (which is common and not significant) but also in the buttock, thigh and calf. Normally it should be possible to raise the limb to 8090 degrees; people with hypermobility can go even further. In disc prolapse with nerve root compression, straight-leg raising may be restricted to less than 30 degrees because of severe pain. At the point where the patient experiences discomfort, passive dorsiflexion of the foot may cause an additional stab of sciatic pain. Buttock pain is immediately relieved; pain may then be re-induced without extending the knee by simply pressing on the lateral popliteal nerve behind the lateral tibial condyle, to tighten it like a bowstring.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q.i.d.
Tags: order 300 mg avapro with amex, avapro 300 mg purchase without prescription, discount 300 mg avapro overnight delivery, avapro 150 mg on line
9 of 10
Votes: 329 votes
Total customer reviews: 329
Testimonials
Nafalem, 21 years: Clinical features the condition may come on gradually, or rapidly following a change in sporting activity (or a change of sports footwear). The patient is blindfolded and instructed to pick up and identify nine objects as rapidly as possible. By then primitive skeletal elements and pre-muscle masses have begun to differentiate in the limbs. The results, even with delayed surgery and quite long grafts, can be gratifying as the radial nerve has a straightforward motor function.
Musan, 60 years: X-rays show pronounced but asymmetrical intervertebral spur formation and bridging throughout the dorsolumbar spine. Autosomal dominant disorders Autosomal dominant disorders are inherited even if only one of a pair of alleles on a non-sex chromosome is abnormal; the condition is said to be heterozygous. Severe examples of club foot are seen in association with genetic conditions such as arthrogryposis, diastrophic dysplasia, FreemanSheldon syndrome and amniotic constriction rings. Gait is important; the patient should also be observed walking with and without any support such as a stick or crutch.
Gunnar, 53 years: Other symptoms are paraesthesiae in the arm or hand and weakness of the muscles of the shoulder, forearm and hand. Arthroscopic repair of an isolated superior labral lesion is successful in the large majority (91%) of patients. Alternatively, bisphosphonates are effective in reducing fracture risk in the context of hypogonadism. Deficit in using executive functions to go beyond automatic activities and plan and carry out an integrated course of action.
Tippler, 52 years: Theoretically 1 in 4 of the children will be homozygous and will therefore develop the disease; 2 out of 4 will be heterozygous carriers of the faulty gene. In long-standing cases, the tissues are thickened and often puckered or folded inwards where a scar or sinus adheres to the underlying bone. Shoulder movements are painless but abduction and elevation may be limited by the fixation of the scapula. Controlled-release melatonin, singly and combined with cognitive behavioural therapy, for persistent insomnia in children with autism spectrum disorders: a randomized placebo-controlled trial.
Hogar, 23 years: The techniques of lengthening are as described earlier and two bones can be dealt with simultaneously. A large embolus leads to the classic signs of pain, pulselessness, paraesthesia, pallor and paralysis. It allows good visualization of both sides of the rotator cuff and the identification of partial and full-thickness tears. The principal first-line chemotherapeutic agents used in osteosarcoma are doxorubicin, cisplatin, ifosfamide and methotrexate.
Tjalf, 64 years: Counselling Patients and families may need expert counselling about (1) the likely outcome of the disorders; (2) what will be required of the family; and (3) the risk of siblings or children being affected. At the prekindergarten visit, identification of at least 4 random letters that are not in alphabetical order is strongly associated with appropriate phonological processing skills needed for reading decoding. However, the deformity first needs to be corrected before a tendon transfer is considered; additionally, the transfer only works if the joints are mobile. Patients should undergo radiological screening of the cervical spine and may require cervico-occipital fusion in the presence of significant instability to prevent cervical myelopathy.

 Contact
Contact Hours
Hours Location
Location